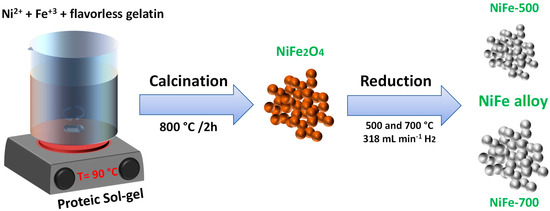
In this study, Ni-Fe alloy nanoparticles were prepared using the proteic sol–gel method, followed by a reduction in H
2 at 500 and 700 °C, namely hereafter as NiFe-500 and NiFe-700, respectively. The morphological, structural, and magnetic properties were tuned via the thermal
[...] Read more.
In this study, Ni-Fe alloy nanoparticles were prepared using the proteic sol–gel method, followed by a reduction in H
2 at 500 and 700 °C, namely hereafter as NiFe-500 and NiFe-700, respectively. The morphological, structural, and magnetic properties were tuned via the thermal treatment in H
2. The samples were studied using XPS, TEM, Mössbauer spectroscopy, DC magnetic measurements, and electrochemical measurements. Ritveld refinements showed that the sample NiFe-500 has FCC (face-centered cubic) and BCC (body-centered cubic) NiFe alloys, while the sample NiFe-700 has only FCC NiFe alloy. For both samples, magnetization measurements in the range of 300–900 K showed the presence of the Griffiths phase, indicating the formation of clusters of either Fe or Ni-Fe alloys rich in Fe. The sample NiFe-500 presented ferromagnetic (FM) transitions at 533, 700, and 834 K, assigned to the alloys Ni
37Fe
63-FCC, Ni
46Fe
54-FCC, and Ni
55Fe
45-FCC, respectively. In contrast, we could not observe the FM transition of the BCC Ni-Fe alloy because of limitations in our experimental setup (T ≤ 900 K). Meanwhile, three FM transitions were observed for the sample NiFe-700 at 480, 655, and 825 K, attributed to the alloys Ni
34Fe
66-FCC, Ni
43Fe
57-FCC, and Ni
54Fe
46-FCC, respectively. At 5 K, the samples NiFe-500 and NiFe-700 have saturation magnetizations of 164.2 and 173.6 emu g
−1, respectively. For application in Oxygen Evolution Reaction catalysis, the samples NiFe-500 and NiFe-700 showed different overpotentials of 319 and 307 mV at 10 mA cm
−2. These low overpotential values indicate a higher electrochemical activity of the FCC Ni-Fe alloy and, for both samples, a superior electrocatalytic activity in comparison to RuO
2 e IrO
2 conventional catalysts. Furthermore, the samples showed high electrochemical stability in chrono potentiometric studies for up to 15 h. This current work highlights that the Ni-Fe alloys produced via the proteic sol–gel and with a reduction in H
2 methods can be promising for OER systems due to their good performance and low costs.
Full article
 Current Oncology
Current Oncology Vaccines
Vaccines Water
Water Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Crystals
IMPACT
Crystals
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Entropy
IMPACT
Entropy
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Biology
IMPACT
Biology
IMPACT Antibiotics
IMPACT
Antibiotics
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Photonics
IMPACT
Photonics
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Catalysts
IMPACT
Catalysts
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Pathogens
IMPACT
Pathogens
IMPACT Axioms
IMPACT
Axioms
IMPACT